Reading Data from Excel
Data-driven testing is a helpful feature for the following scenarios:
- When business users would like to have ownership over the test data in your automated tests
- When you have multiple data permutations and you would like to loop through data sets
- When you would like to perform various calculations on your data and use Excel as a method of deriving the fields
Automation has Read and Write test steps to read data from an Excel sheet or a database and write data to an Excel spreadsheet.
This page describes how to configure Automation to test using data from Excel. You can also refer to Write Data Into Excel for more information.
To read from the Excel sheet, first, get your Excel file ready on your local machine.
Note: It is a good practice to save the file in the templates folder in your workspace.
Next, read the Excel file into your test case using Add Parameter Value Source. You can do this from any test step, but you will often find it helpful to do it on your For Each test step if you use one. (For Each is often used within Data-Driven Testing to iterate the same action through each data row.)
To read the Excel data into your Test Case, click the Add Parameter Value Source icon (
This will add the following new section to your Test Step:
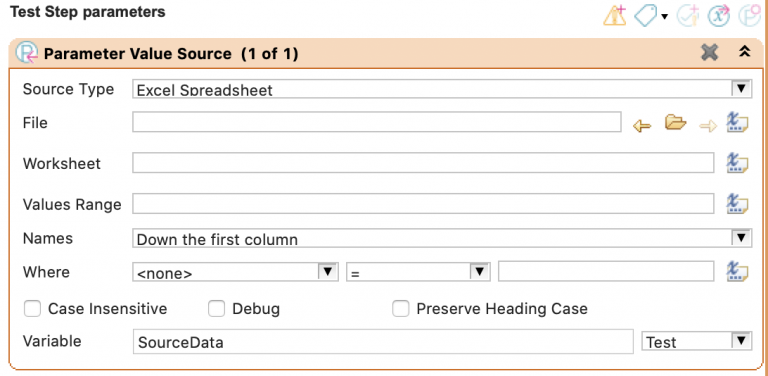
You can populate this as follows:
Step 1: If you are on a Windows machine, navigate to your Excel file and highlight the range of cells you want to read into Provar. Then select CTRL+C to copy. Navigate to Provar and select the Populate From File icon (
Step 2: If you are using a Mac, you will need to populate File, Worksheet, and Values Range manually. Use File Chooser (
Step 3: In the Name field, select the orientation of the headers.
Step 4: In the Where field, specify any filter you want to be applied to the data being imported.
Step 5: In Variable, specify your preferred object name for the results (the default is ExcelData).
Step 6: Parameterize the Test Case.
Add to Test Case
Once you have read the data from the Excel sheet, you need to use it in your test case. This is typically done using a For Each or While test step to loop through multiple rows and create a test step to make the data
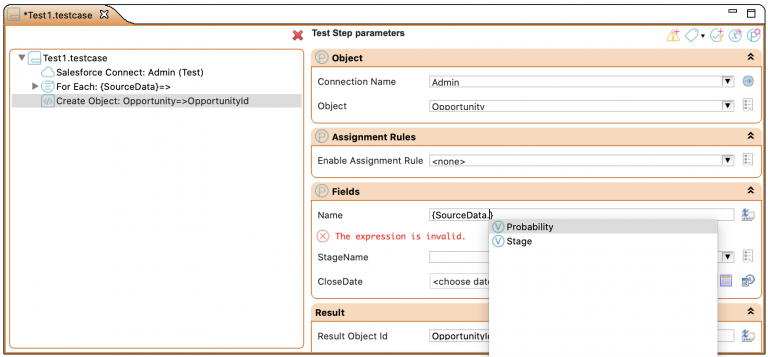
Step 1: Use Content Assist to access the fields in the SourceData object.
Step 2: Specify the list Name (e.g., SourceData) and the Value Name For Each test step. (The Value Name is the name for the current iteration.)
Step 3: Use the full stop to access the column headings.
Load Multiple Records
To increase efficiency, Automation allows you to loop through rows of a spreadsheet to iterate upon the data. This means that the same actions will be performed for every row in the spreadsheet. By using a single test case for many input parameters, you can save time and minimize errors.
For example, this set of data will load in three rows of data.

In order to make the test run through all the records, we need a test step that will loop through the new rows we added. The For Each step in the Test Palette allows us to execute the steps for each record.
Step 1: Drag For Each step from the Test Palette into your test.

Step 2: Now that we have the For Each step added to the test, we need to fill in the required fields. The first field is the List field. Our list is already loaded, so use Content Assist to add SourceData as the list.

Step 3: Now that we’ve provided the list of records, let’s look at the other fields.
- From Item tells the loop we’re starting with the first record
- Value Name field is the name used to refer to each row of data
- Continue on Failure will keep looping through rows even if one iteration fails
Since we’re referring to rows of data, let’s call this Row for the value name.

Step 4: Now that we’ve set the parameters, you need to add the steps you wish to repeat inside the For Each step. To maintain order, make sure to select all of the steps and move them together.
Step 5: Before running the test, we need to update the steps that refer to our rows. In the For Each settings, we provided the Value Name as Row. Now we can call it in the test steps we want to loop. Use Content Assist to call Row for the value. After choosing Row, use dot notation to refer to the field you wish to use.

Step 6: Update the other steps under For Each with the Row variable and the dot notation for the correct field. When you are done, your test case should look something like this.

Now that your test is set up, it will execute all of the steps within the For Each loop for all of the rows of data on your spreadsheet.
For more information on Data-Driven Testing, check out the University of Provar course Provar Automation Essentials: Data-Driven Testing
- Provar Automation
- Installing Provar Automation
- Updating Provar Automation
- Using Provar Automation
- API Testing
- Behavior-Driven Development
- Creating and Importing Projects
- Creating Test Cases
- Custom Table Mapping
- Functions
- Debugging Tests
- Defining a Namespace Prefix on a Connection
- Defining Proxy Settings
- Environment Management
- Exporting Test Cases into a PDF
- Exporting Test Projects
- Override Auto-Retry for Test Step
- Managing Test Steps
- Namespace Org Testing
- NitroX
- Provar Automation
- Provar Test Builder
- Refresh and Recompile
- Reintroduction of CLI License Check
- Reload Org Cache
- Reporting
- Running Tests
- Searching Provar with Find Usages
- Secrets Management and Encryption
- Setup and Teardown Test Cases
- Tags and Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
- Test Cycles
- Test Plans
- Testing Browser Options
- Tooltip Testing
- Using the Test Palette
- Using Custom APIs
- Callable Tests
- Data-Driven Testing
- Page Objects
- Block Locator Strategies
- Introduction to XPaths
- Creating an XPath
- JavaScript Locator Support
- Label Locator Strategies
- Maintaining Page Objects
- Mapping Non-Salesforce fields
- Page Object Operations
- ProvarX™
- Refresh and Reselect Field Locators in Test Builder
- Using Java Method Annotations for Custom Objects
- Applications Testing
- Provar Manager
- How to Use Provar Manager
- Provar Manager Setup
- Provar Manager Integrations
- Release Management
- Test Management
- Test Operations
- Provar Manager and Provar Automation
- Setting Up a Connection to Provar Manager
- Object Mapping Between Automation and Manager
- How to Upload Test Plans, Test Plan Folders, Test Plan Instances, and Test Cases
- Provar Manager Filters
- Uploading Callable Test Cases in Provar Manager
- Uploading Test Steps in Provar Manager
- How to Know if a File in Automation is Linked in Test Manager
- Test Execution Reporting
- Metadata Coverage with Manager
- Provar Grid
- DevOps
- Introduction to Provar DevOps
- Introduction to Test Scheduling
- Apache Ant
- Configuration for Sending Emails via the Automation Command Line Interface
- Continuous Integration
- AutoRABIT Salesforce DevOps in Provar Test
- Azure DevOps
- Running a Provar CI Task in Azure DevOps Pipelines
- Configuring the Automation secrets password in Microsoft Azure Pipelines
- Parallel Execution in Microsoft Azure Pipelines using Multiple build.xml Files
- Parallel Execution in Microsoft Azure Pipelines using Targets
- Parallel execution in Microsoft Azure Pipelines using Test Plans
- Bitbucket Pipelines
- CircleCI
- Copado
- Docker
- Flosum
- Gearset
- GitHub Actions
- Integrating GitHub Actions CI to Run Automation CI Task
- Remote Trigger in GitHub Actions
- Parameterization using Environment Variables in GitHub Actions
- Parallel Execution in GitHub Actions using Multiple build.xml Files
- Parallel Execution in GitHub Actions using Targets
- Parallel Execution in GitHub Actions using Test Plan
- Parallel Execution in GitHub Actions using Job Matrix
- GitLab Continuous Integration
- Travis CI
- Jenkins
- Execution Environment Security Configuration
- Provar Jenkins Plugin
- Parallel Execution
- Running Provar on Linux
- Reporting
- Salesforce DX
- Git
- Team Foundation Server
- Version Control
- Masking Provar Credentials on CI
- Salesforce Testing
- Best Practices
- Salesforce Connection Best Practices
- Improve Your Metadata Performance
- Testing Best Practices
- Automation Planning
- Supported Testing Phases
- Provar Naming Standards
- Test Case Design
- Create records via API
- Avoid using static values
- Abort Unused Test Sessions/Runs
- Avoid Metadata performance issues
- Increase auto-retry waits for steps using a global variable
- Create different page objects for different pages
- The Best Ways to Change Callable Test Case Locations
- Working with the .testProject file and .secrets file
- Best practices for the .provarCaches folder
- Best practices for .pageObject files
- Troubleshooting
- How to Use Keytool Command for Importing Certificates
- Browsers
- Configurations and Permissions
- Connections
- DevOps
- Error Messages
- Provar Manager 3.0 Install Error Resolution
- Provar Manager Test Case Upload Resolution
- Administrator has Blocked Access to Client
- JavascriptException: Javascript Error
- macOS Big Sur Upgrade
- Resolving Failed to Create ChromeDriver Error
- Resolving Jenkins License Missing Error
- Resolving Metadata Timeout Errors
- Test Execution Fails – Firefox Not Installed
- Selenium 4 Upgrade
- Licensing, Installation and Firewalls
- Memory
- Test Builder and Test Cases
- Release Notes